Plate-by-plate method




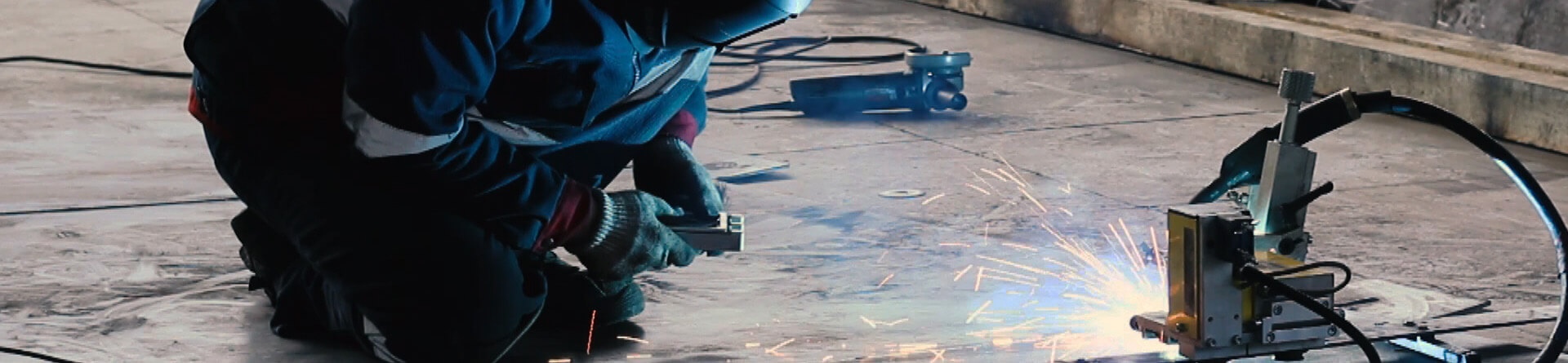
The first method of construction of storage tanks is the plate-by-plate assembly of the shells, bottoms and roofs. It implies that the shell plate of maximum size 2500×10000 mm and the bottom sheets are prepared at the factory site, they are rolled to the radius, stipulated by the design project. Then the sheet elements are packed in a special way to be prepared for transportation. Shell and bottom assembly (welding) is carried out on the construction site.
The main factor determining the quality of the tank metal structures, produced by this method, is strict provision of their shape (referred to the design project), and the set of technological decisions, preventing residual distortion of the metal frameworks in the course of edging and transportation.
The basic stages of plate-by-plate production of vertical tanks’ shells and bottoms are as follows:
1. Preparation procedures
The first stage includes preparation of shell and bottom plates. This stage ensures meeting the planned dimensions and geometric parameters. Pre-welding edging is also done.
Extreme shape deviations of the plates are controlled in the course of preparation. The company’s Technical regulations set the maximum width deviation within the limits of ±0,5 mm.
2. Rolling
Rolling is done afterwards, meeting the radius, planned by the engineering design project. Rolling gives the cylindrical shape to the tank shell while installation is carried out.
Plate-bending machines IB2426 and XZC 3000/25 are used by EuroTankWorks for rolling sheets up to 40 mm and 25 mm correspondingly. This equipment gives the opportunity to make the radius equal within the whole length of the plate.
The radius is checked by the pattern. The clear gap between the pattern (2 m) in an arc and the bent plate surface should not exceed 3 mm.
Another rolling quality parameter is the waviness of the front edge. It may not exceed 4 mm on the whole length of the sheet. The waviness parameter per 1 m of sheet length should fall into the limits of 2 mm.
Packing.
The plate frameworks of the shells are packed and carried in special lodgments (cradles).
Lodgments are constructed in a way, providing:
- Keeping the radius of rolled sheet as a result of exact conformance of the lodgment to its geometric parameters;
- Tough fixing of the plate frameworks, aimed at avoiding edges’ damage;
- The units’ safety in the course of transportation, preventing residual deformation.
The bottom parts are packed and transported in containers, constructed in accordance with their types and dimensions.
Tank roof metal frameworks fabrication:
Production technologies for the roof metalwork of a storage tank vary depending on its type, determined by the design project. In relation to the type and dimensions of the tank, and other specific features as well, either permanent-type roofs or floating roofs are used. Permanent roofs include either frameless or framed roofs conical or spherical in shape.
Coiling method




This method is one of the two industrial approaches for manufacturing the metal structures of a storage tank. It implies that tank shell, bottom and roof are brought to the construction site in the form of coiled strip panels, meant for welding. The advantages of this method are to be seen in making the tank installation period 3-4 times shorter as a result of cutting down the volume of welding procedures in the building area by about 80 % at the average and providing high quality of welding joints due to the use of two-side automatic welding.
Strip panels are produced from steel plates of modular size 1500×6000 mm.
Panels are automatically welded on a special coiling machine. It consists of welding and assembly sites – top and bottom level, edging tumbler and rolling (coiling) device.
Coiling machine’s operation is performed in two basic schemes (upper and lower coiling). Lower coiling is meant for manufacturing tank shells up to 18 mm thickness, upper coiling is used for thicknesses not exceeding 16 mm.
The length of the coils amounts to 18 m, the weight is adjusted to the load-lifting capacity of motive power.
Stages of strip panel manufacturing by coiling method:
- designing the technological structure;
- arranging the plates according to the detailed metal framework graphical drafts;
- welding and coiling;
- preparation of coils for transportation.
Preparation of technological frame:
Before welding the strip panels a special frame is prepared, on which the sheets will be coiled. The diameter of the frame should not be less than 2.6 m, and its length should be equal to the height of the storage tank shell.
Shaft staircase is often used as a technological frame for coiling the shell. This is usually applied for tanks not exceeding 2000 m³ of loading capacity. In this case metal economy is provided.
Arranging the strip panel sheets:
Arranging of shell plates, bottom and roof is carried out on the upper welding and assembly level of the coiling machine. In the course of arranging process the prepared plates are laid out on the site in accordance with the graphic drafts and are fixed with the installation instruments.
Coilable shell strip panels must have a certain technological allowance in length, which enables to assemble the installation joints.
Welding and coiling of the strip panels:
Welding is the basic stage of storage tank fabrication, as regards coiling method. We use automatic two-side welding of fore and crosscut joints. At first the original seam is welded on the top welding and assembly level of the coiling machine, then the strip panel is rewound through the edging tumbler and the second seam is done at the bottom level.
The order of coiling the strip panels of different tank frames is planned in reverse sequence of unrolling them in the course of installation. The shell plates are coiled in a way, that implies that they are meant to be unrolled in clockwise direction.
To ensure quality of the welding joints our factory applies a complex of measures.
The welding procedures were originally worked out and tested by our Welding Laboratory. They were taken as the basis for the Welding Operating Conditions, which determine the requirements for welding joints and the order of technological operations as regards the types and the thicknesses of metal roll, type of the weld, steel edge preparation and other parameters.
Our Welding Operating Conditions represent the basic operation document, determining the work of welders and the quality control of the joints.
Execution of the Welding Operating Conditions is controlled by the General Welding Operator Service and Quality Control Department.
As a result of thorough work through and strict execution of the Welding Operating Conditions we were able to provide the highest quality of the welding joints. It is considered to be one of the main advantages of the metal frameworks, produced by the company. It often happens that imperfections of welding technology or/and its violations cause a range of serious problems, as:
- the smooth connection of the weld and the main metal is not provided.
- main metal undercuts and cold laps appear.
- defects in welding joints appear: cracks, ripples, gas pockets and their chains, burn-through and blowholes.
As a result of these, full strength of the welding joint does not meet the standards and may cause welding deformations, bringing about bulges, dents and canning.